4.4 Lab Exercises
Overview
This lab will walk us through the process of annotating a genome for genes using the BRAKER2 pipeline.
We will do three major things in this lab:
Install BRAKER
Collect all of the available Quercus peptides that exist, and align them to our haplotype references
Run the BRAKER2 pipeline using orthologous gene evidence to train AUGUSTUS and build an annotation set
“Be for real, don’t be a stranger”` - Spice Girls
Task A
First, we need to produce a softmasked genome. Softmasked means we convert any repetitive region of the genome to a lowercase letter. BRAKER2, our gene annotation pipeline, prefers softmasked genomes so it can “ignore” those regions for gene annotation.
Bedtools has a tool that can do this for us.
Using the the .gff3 you produced as part of EDTA, e.g. (toomers.hap1.fasta.mod.EDTA.TEanno.gff3),
run bedtools maskfasta with the -soft flag to create a softmasked genome fasta file.
Task B
Next we will run the BRAKER2 pipeline to annotate genes in the reference haplotypes you have assembled. In the absence of RNA-seq data, we will need to rely on closely related peptides for gene prediction. Luckily, there are three other Quercus genomes that exist: lobata, robur, and rubra. We can leverage the gene annotations from these three genomes, as well as the seemingly high degree of conservation across the Quercus genus, to train gene predictors and build an annotation set.
First, read the BRAKER2 github page. We will be using “Pipeline C” that leverages orthologs of any evolutionary distance to train AUGUSTUS.
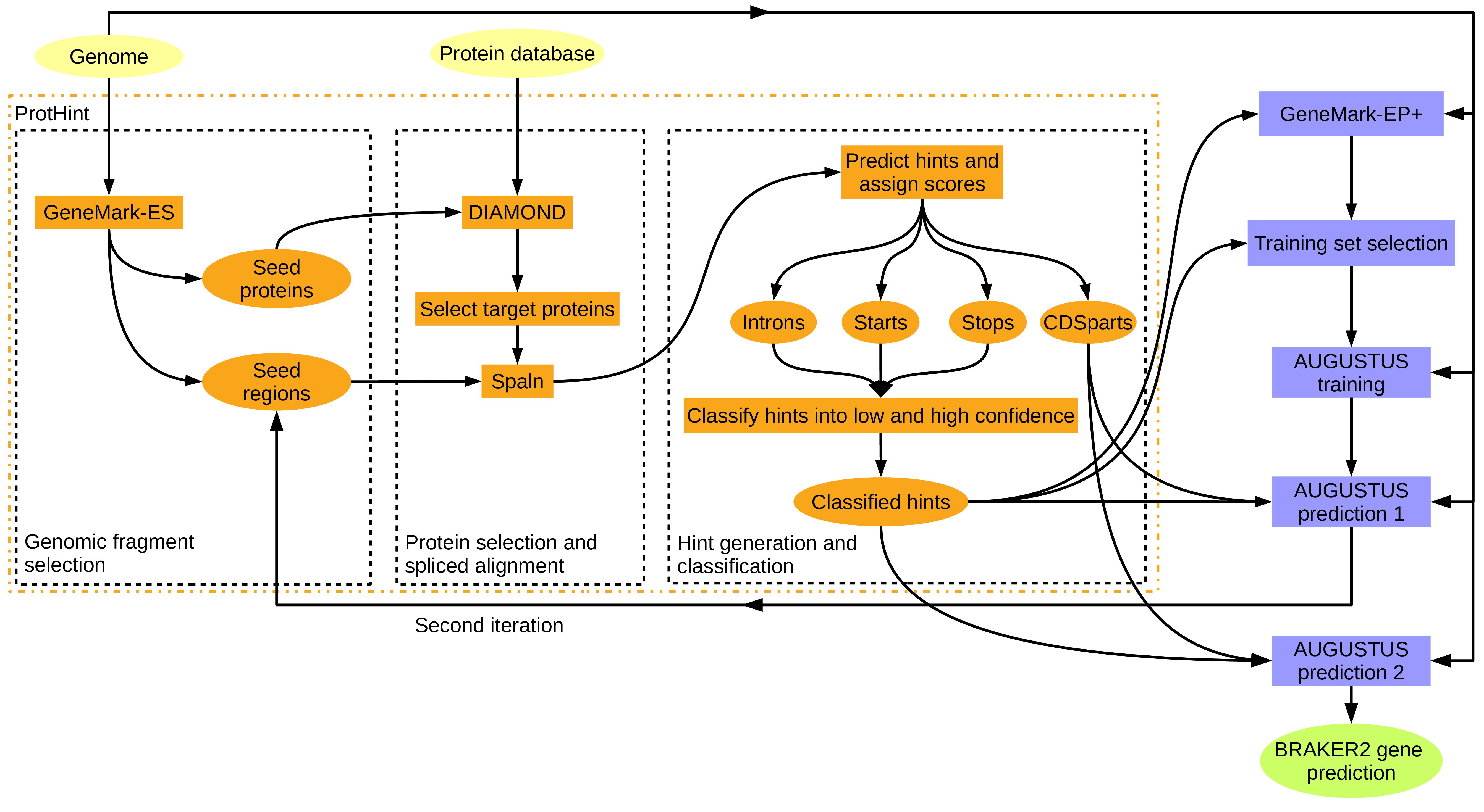
Image Source: BRAKER GitHub Page
You can install BRAKER2 with conda, with the caveat that it is sometimes a few versions behind. That will be fine for us, though.
Create a new conda environment called “braker”, then install BRAKER2 using Conda.
First, collect the protein fasta annotations for Quercus rubra, robur, lobata. Make sure they’re proteins/peptides! Use Phytozome and/or any other means you need to. Concatenate them into a single .fasta file, like this:
cat species1.fasta species2.fasta species3.fasta > quercus_proteins.fasta
Then, run BRAKER2 using the “proteins from any evolutionary distance” pipeline. Make sure you use the softmask flag!